What does a future Civil Engineer from Uniandes study?
Our curriculum in Civil Engineering has the following knowledge areas:
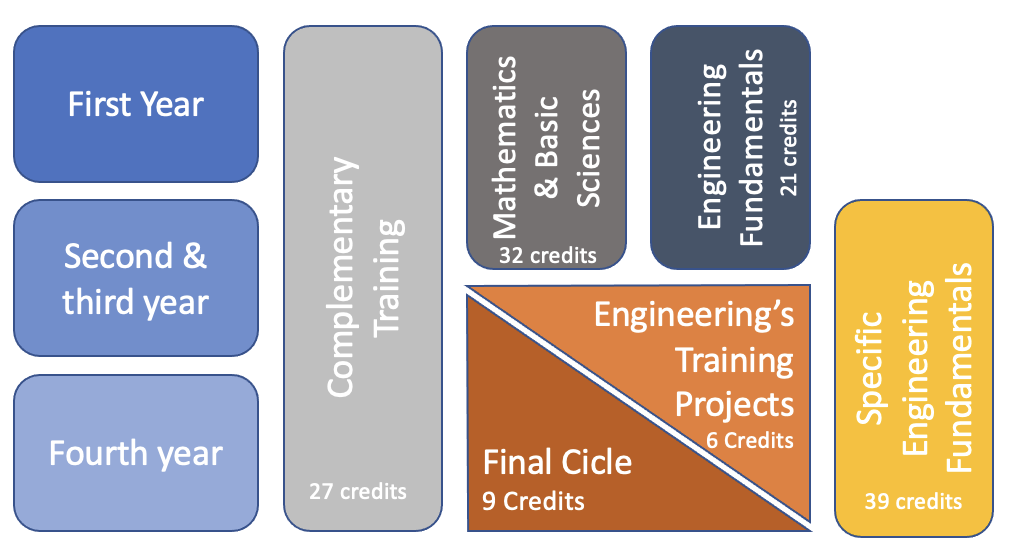
- Mathematics and Basic Sciences: Includes foundation courses in science and mathematics, such as calculus, physics, and chemistry.
- Engineering Fundamentals: Includes foundation courses in science and mathematics, such as calculus, physics, and chemistry.
- Specific Engineering Fundamentals: These include the specific courses of the program, which lay the foundations for the formal exercise of the profession in each of the areas of Civil Engineering.
- Engineering's Training Projects: They include the courses final project of design and project of degree.
- Final Cycle: Consisting of deepening elective courses.
- General Education: Cycle transversal to all the programs of the Universidad de los Andes, including comprehensive training courses and courses in citizenship.
In the specific training in Civil Engineering, you will have the possibility to choose the area in which you want to deepen, among the following:
- Geotechnical: includes the study of the behavior of soils, rocks and civil works built on them. The application of advanced methods of land prospecting (geophysical methods). The modeling and simulation in the computer of the history of efforts and deformations of a soil and the modeling of the behavior of geotechnical works on a reduced scale in a centrifuge.
- Structural and Seismic: covers the study and application of structural analysis and design methods, seismic risk analysis and earthquake-resistant design of structures, and the study of neotectonics and analysis of the states of stress and deformation of the earth's crust.
- Road Infrastructure: includes the design of roads, the analysis of pavement structures, the study of the behavior of water in road structures, compaction theories, urban and interurban transport planning, transport economics, the operation of transport and public transport.
- Infrastructure Systems: focuses on the analysis and modeling of engineering problems from a systemic perspective and with an emphasis on uncertainty management. Within its scope are, among others, network modeling (e.g., transportation, energy distribution); the behavior of systems over time; decision-making processes in Engineering; and financial models..
- Transportation Engineering: it is focused on the planning, design, analysis and evaluation of different transportation systems and their components, from a holistic and multidisciplinary perspective.
- Water Resources: it is made up of the analysis of the behavior of hydraulic structures through physical laboratory models, the experimental analysis of the characteristics of pipes and accessories, the hydrological and hydraulic modeling of complex lagoon systems, and the implementation of hydrodynamic models, analysis programs and design of pipelines and distribution networks.
- Engineering and Management Construction: it deals with the understanding of the design and execution of construction projects, the study of construction processes, calculation of project times and costs, and the control of quality, cost and time characteristics, and the use of computational tools in construction projects.
Tipo de elemento:
Enlace
Orden:
2